On December 17, 2024, Joonkyung Lee (이준경) from Yonsei University gave a talk on using Lorentzian polynomials to prove a non-trivial upper bound on the number of graph homomorphisms at the Discrete Math Seminar. The title of his talk was “Counting homomorphisms in antiferromagnetic graphs via Lorentzian polynomials“.
Joonkyung Lee (이준경), Counting homomorphisms in antiferromagnetic graphs via Lorentzian polynomials
An edge-weighted graph $G$, possibly with loops, is said to be antiferromagnetic if it has nonnegative weights and at most one positive eigenvalue, counting multiplicities. The number of graph homomorphisms from a graph $H$ to an antiferromagnetic graph $G$ generalises various important parameters in graph theory, including the number of independent sets and proper vertex colourings.
We obtain a number of new homomorphism inequalities for antiferromagnetic target graphs $G$. In particular, we prove that, for any antiferromagnetic $G$,
$|\mathrm{Hom}(K_d, G)|^{1/d} ≤ |\mathrm{Hom}(K_{d,d} \setminus M, G)|^{1/(2d)}$
holds, where $K_{d,d} \setminus M$ denotes the complete bipartite graph $K_{d,d}$ minus a perfect matching $M$. This confirms a conjecture of Sah, Sawhney, Stoner and Zhao for complete graphs $K_d$. Our method uses the emerging theory of Lorentzian polynomials due to Brändén and Huh, which may be of independent interest.
Joint work with Jaeseong Oh and Jaehyeon Seo.
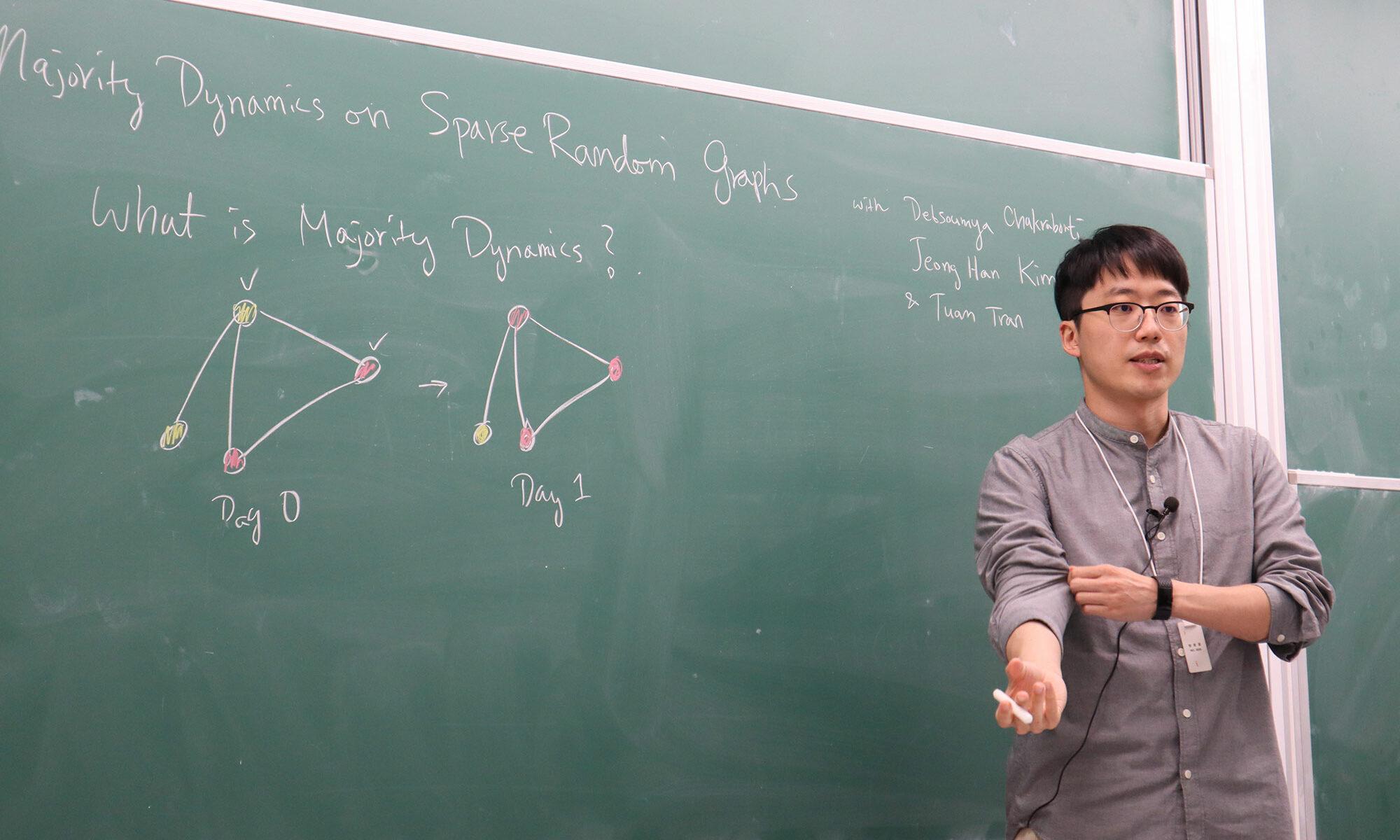
Joonkyung Lee (이준경) gave a talk about the majority dynamics on sparse random graphs at the Discrete Math Seminar
On October 12, 2021, Joonkyung Lee (이준경) from the Hanyang University gave a talk about the majority dynamics on sparse random graphs. The title of his talk was “Majority dynamics on sparse random graphs“.
Joonkyung Lee (이준경), Majority dynamics on sparse random graphs
Majority dynamics on a graph $G$ is a deterministic process such that every vertex updates its $\pm 1$-assignment according to the majority assignment on its neighbor simultaneously at each step. Benjamini, Chan, O’Donnell, Tamuz and Tan conjectured that, in the Erdős-Rényi random graph $G(n,p)$, the random initial $\pm 1$-assignment converges to a $99\%$-agreement with high probability whenever $p=\omega(1/n)$.
This conjecture was first confirmed for $p\geq\lambda n^{-1/2}$ for a large constant $\lambda$ by Fountoulakis, Kang and Makai. Although this result has been reproved recently by Tran and Vu and by Berkowitz and Devlin, it was unknown whether the conjecture holds for $p< \lambda n^{-1/2}$. We break this $\Omega(n^{-1/2})$-barrier by proving the conjecture for sparser random graphs $G(n,p)$, where $\lambda’ n^{-3/5}\log n \leq p \leq \lambda n^{-1/2}$ with a large constant $\lambda’>0$.
Joint work with Debsoumya Chakraborti, Jeong Han Kim and Tuan Tran.
Extremal and Probabilistic Combinatorics (2021 KMS Spring Meeting)
A special session “Extremal and Probabilistic Combinatorics” at the 2021 KMS Spring Meeting is organized by Tuan Tran.
URL: https://www.kms.or.kr/meetings/spring2021/
Speakers and Schedule
All talks are on April 30.
- [9:00 am] Joonkyung Lee (이준경), University College London
- Majority dynamics on sparse random graphs
- [9:30 am] Dong Yeap Kang (강동엽), Unversity of Birmingham
- The Erdős-Faber-Lovász conjecture and related results
- [10:00 am] Jinyoung Park (박진영), IAS
- The threshold for the square of a Hamilton cycle
- [10:50 am] Debsoumya Chakraborti, IBS Discrete Mathematics Group
- Generalized graph saturation
- [11:20 am] Jaehoon Kim (김재훈), KAIST
- Resolution of the Oberwolfach problem
- [11:50 am] Hong Liu, University of Warwick
- Sublinear expanders and its applications
Abstracts
Debsoumya Chakraborti, Generalized graph saturation
Graph saturation is one of the oldest areas of investigation in extremal combinatorics. A graph G is called F-saturated if G does not contain a subgraph isomorphic to F, but the addition of any edge creates a copy of F. We resolve one of the most fundamental questions of minimizing the number of cliques of size r in a $K_s$-saturated graph for all sufficiently large numbers of vertices, confirming a conjecture of Kritschgau, Methuku, Tait and Timmons. We further prove a corresponding stability result. This talk will be based on joint work with Po-Shen Loh.
Jaehoon Kim (김재훈), Resolution of the Oberwolfach problem
The Oberwolfach problem, posed by Ringel in 1967, asks for a decomposition of $K_{2n+1}$ into edge-disjoint copies of a given 2-factor. We show that this can be achieved for all large n. We actually prove a significantly more general result, which allows for decompositions into more general types of factors.
Dong Yeap Kang (강동엽), The Erdős-Faber-Lovász conjecture and related results
A hypergraph is linear if every pair of two distinct edges shares at most one vertex. A longstanding conjecture by Erdős, Faber, and Lovász in 1972, states that the chromatic index of any linear hypergraph on n vertices is at most n.
In this talk, I will present the ideas to prove the conjecture for all large n. This is joint work with Tom Kelly, Daniela Kühn, Abhishek Methuku, and Deryk Osthus.
Joonkyung Lee (이준경), Majority dynamics on sparse random graphs
Majority dynamics on a graph G is a deterministic process such that every vertex updates its {-1,1}-assignment according to the majority assignment on its neighbor simultaneously at each step. Benjamini, Chan, O’Donnell, Tamuz and Tan conjectured that, in the Erdős-Rényi random graph G(n,p), the random initial {-1,1}-assignment converges to the unanimity with high probability whenever p>> 1/n.
This conjecture was firstly confirmed for $p>Cn^{-1/2}$ for a large constant C>0 by Fountoulakis, Kang and Makai. Although this result has been reproved recently by Tran and Vu and by Berkowitz and Devlin, none of them managed to extend it beyond the barrier $p>Cn^{-1/2}$. We prove the conjecture for sparser random graphs G(n,p), where $Dn^{-3/5}\log n < p < C n^{-1/2}$ with a large constant D>0.
Joint work with Debsoumya Chakraborti, Jeong Han Kim and Tuan Tran.
Hong Liu, Sublinear expanders and its applications
I will review the history of sublinear expander and present some recent applications, which lead to resolutions of several long-standing problems in sparse graphs embeddings.
Jinyoung Park (박진영), The threshold for the square of a Hamilton cycle
We will talk about a recent result of Jeff Kahn, Bhargav Narayanan, and myself stating that the threshold for the random graph G(n,p) to contain the square of a Hamilton cycle is $1/\sqrt n$, resolving a conjecture of Kühn and Osthus from 2012. The proof idea is motivated by the recent work of Frankston and the three aforementioned authors on a conjecture of Talagrand — “a fractional version of Kahn-Kalai expectation threshold conjecture.”
Joonkyung Lee (이준경) gave online talks on the Ramsey multiplicity and common graphs at the Discrete Math Seminar
On November 30 and December 2, 2020, Joonkyung Lee (이준경) from University College London gave two online talks on the Ramsey multiplicity and common graphs at the Discrete Math Seminar organized by Jaehoon Kim at KAIST. The titles of his talks are “On Ramsey multiplicity” and “On common graphs“.
(The photo above was taken earlier in his other seminar talk.)
Joonkyung Lee (이준경), On common graphs
A graph $H$ is common if the number of monochromatic copies of $H$ in a 2-edge-colouring of the complete graph $K_n$ is minimised by the random colouring. Burr and Rosta, extending a famous conjecture by Erdős, conjectured that every graph is common. The conjectures by Erdős and by Burr and Rosta were disproved by Thomason and by Sidorenko, respectively, in the late 1980s.
Despite its importance, the full classification of common graphs is still a wide open problem and has not seen much progress since the early 1990s. In this lecture, I will present some old and new techniques to prove whether a graph is common or not.
Joonkyung Lee (이준경), On Ramsey multiplicity
Ramsey’s theorem states that, for a fixed graph $H$, every 2-edge-colouring of $K_n$ contains a monochromatic copy of $H$ whenever $n$ is large enough. Perhaps one of the most natural questions after Ramsey’s theorem is then how many copies of monochromatic $H$ can be guaranteed to exist. To formalise this question, let the Ramsey multiplicity $M(H;n)$ be the minimum number of labelled copies of monochromatic $H$ over all 2-edge-colouring of $K_n$. We define the Ramsey multiplicity constant $C(H)$ is defined by $C(H):=\lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}\frac{M(H,n)}{n(n-1)\cdots(n-v+1)}$. I will discuss various bounds for C(H) that are known so far.
Joonkyung Lee (이준경) gave a talk on norms defined from graphs at the Discrete Math Seminar
On October 21, 2020, Joonkyung Lee (이준경) from University College London gave a talk at the Discrete Math Seminar on norms defined from graphs motivated by Sidorenko’s conjecture and Gowers norms on extremal combinatorics, unifying two seemingly different concepts of real-norming graphs and complex-norming graphs. The title of his talk was “On graph norms for complex-valued functions“. Joonkyung Lee will stay at the IBS discrete mathematics group for several weeks from October 19.
Joonkyung Lee (이준경), On graph norms for complex-valued functions
For any given graph $H$, one may define a natural corresponding functional $\|.\|_H$ for real-valued functions by using homomorphism density. One may also extend this to complex-valued functions, once $H$ is paired with a $2$-edge-colouring $\alpha$ to assign conjugates. We say that $H$ is real-norming (resp. complex-norming) if $\|.\|_H$ (resp. there is $\alpha$ such that $\|.\|_{H,\alpha}$) is a norm on the vector space of real-valued (resp. complex-valued) functions. This generalises Gowers norms, a widely used tool in extremal combinatorics to quantify quasirandomness.
We unify these two seemingly different notions of graph norms in real- and complex-valued settings, by proving that $H$ is complex-norming if and only if it is real-norming. Our proof does not explicitly construct a suitable $2$-edge-colouring $\alpha$ but obtain its existence and uniqueness, which may be of independent interest.
As an application, we give various example graphs that are not norming. In particular, we show that hypercubes are not norming, which answers the only question appeared in Hatami’s pioneering work in the area that remained untouched. This is joint work with Alexander Sidorenko.