On November 5, 2020, Daniel Cranston from Virginia Commonwealth University gave a talk on the condition of the maximum average degree for a graph to have a partition of its vertex set into an independent set and a set inducing a forest consisting of components of small size at the Virtual Discrete Math Colloquium. The title of his talk was “Vertex Partitions into an Independent Set and a Forest with Each Component Small“.
Daniel Cranston, Vertex Partitions into an Independent Set and a Forest with Each Component Small
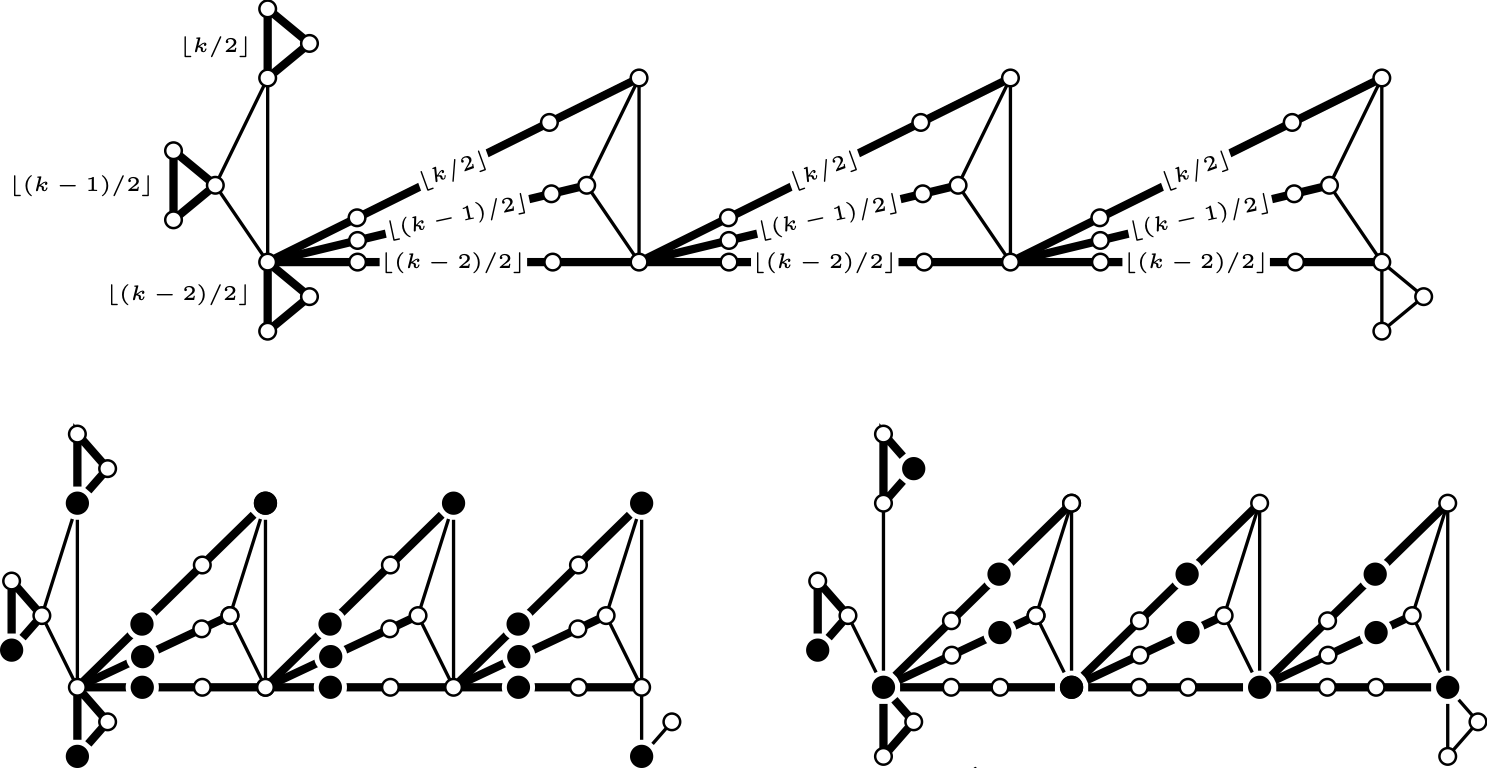
For each integer $k\ge 2$, we determine a sharp bound on
$\operatorname{mad}(G)$ such that $V(G)$ can be partitioned into sets $I$ and $F_k$, where $I$ is an independent set and $G[F_k]$ is a forest in which each component has at most k vertices. For each $k$ we construct an infinite family of examples showing our result is best possible. Hendrey, Norin, and Wood asked for the largest function $g(a,b)$ such that if $\operatorname{mad}(G) < g(a,b)$ then $V(G)$ has a partition into sets $A$ and $B$ such that $\operatorname{mad}(G[A]) < a$ and $\operatorname{mad}(G[B]) < b$. They specifically asked for the value of $g(1,b)$, which corresponds to the case that $A$ is an independent set. Previously, the only values known were $g(1,4/3)$ and $g(1,2)$. We find the value of $g(1,b)$ whenever $4/3 < b < 2$. This is joint work with Matthew Yancey.